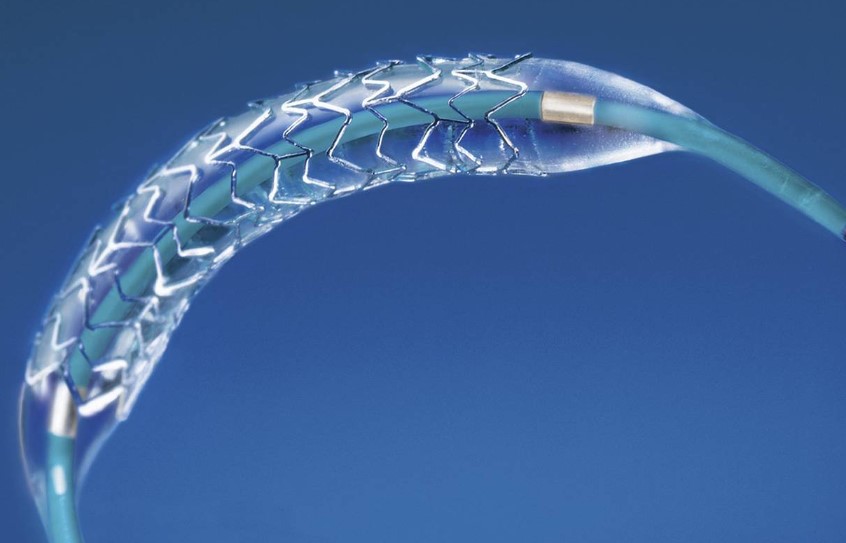
Medical technology has made numerous innovations in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. It includes the development of the cardiac stent. To reestablish blood flow to the heart, a heart stent is a tiny, mesh-like tube that is put into constricted or obstructed blood vessels. Heart stents have transformed the way that heart diseases are treated, but before opting for this procedure, you must fully comprehend what it entails. Let’s look at some fascinating facts given by a cardiologist in Karachi that are important to know before obtaining a cardiac stent.
1- Heart Stents and Their Purpose
Heart stents primarily address coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition that occurs due to the buildup of plaque in the arteries responsible for supplying blood to the heart. This accumulation of plaque can restrict blood flow and lead to various cardiovascular problems. The stent functions as a scaffold, holding the artery open and enabling unhindered blood flow. Enhancing blood circulation minimizes the risk of a heart attack and alleviates angina.
2- Different Types of Stents
Heart stents come in two primary varieties: drug-eluting stents and bare-metal stents. The standard kind of stent is built of metal alloys and is called a “bare metal” stent. Contrarily, drug-eluting stents have drugs coated on them to help prevent the growth of scar tissue and lower the possibility of the artery re-narrowing. Based on your unique circumstances, your doctor will advise you on the best kind of stent.
3- The Procedure: Insertion of a Heart Stent
Coronary angioplasty, also referred to as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is the procedure used to place a cardiac stent. To access the blocked artery during the treatment, a catheter is inserted through a blood vessel, typically in the wrist or groin. Before inserting the stent to keep the artery open, a little balloon at the end of the catheter is inflated to widen the restricted vessels. The stent remains in place after the balloon has been deflated and removed.
4- Potential Risks and Complications
Even though heart stent surgeries are largely risk-free, you should be aware of any possible dangers and problems. These might include the possibility of bleeding, infection, blood vessel damage, adverse reactions to drugs or tools used, or even the chance of having a heart attack or stroke. It is critical to go over these possible hazards with your doctor and compare them to the procedure’s advantages.
5- Post-Stent Care and Medications
Your doctor will prescribe drugs to control other heart diseases, lower cholesterol, and lessen the risk of blood clots after you receive a cardiac stent. To ensure the long-term success of the stent and preserve heart health, it is essential to adhere to your doctor’s recommendations for medications, lifestyle modifications, and routine checkups.
6- Lifestyle Modifications
Coronary artery disease cannot be cured by receiving a cardiac stent. Your overall cardiovascular health will significantly improve as a result of lifestyle changes. Adopting a heart-healthy diet, getting regular exercise, quitting smoking, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight is crucial. These lifestyle adjustments can lower the risk of developing future heart issues and prevent the arteries from getting any narrower. Adopting specific lifestyle changes is essential for maintaining the effectiveness of a cardiac stent over the long term, as well as for enhancing overall cardiovascular health. Making proactive adjustments to your everyday routines and behaviors can have a big impact on your heart health, in addition to medical intervention.
7- Long-Term Outcomes and Effectiveness
Coronary artery disease symptoms can be significantly reduced, and blood flow can be improved, with heart stents. The long-term success of a stent, however, depends on several variables, including the patient’s general health, the size of the stent, the location of the blockage, and the person’s dedication to medication and lifestyle adjustments. To guarantee the stent continues to operate efficiently, routine follow-up appointments and monitoring are required.
8- Alternative Treatment Options
Heart stents are a widespread and reliable method of treating coronary artery disease, although they might only be appropriate for some. In some circumstances, other treatments, including coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), may be advised. CABG involves utilizing blood vessels from other parts of the body to circumvent the blocked artery. To choose the best course of action for your unique illness, it is crucial to have an honest conversation with your doctor.
Conclusion
Heart stents have transformed how coronary artery disease is treated and have significantly improved the quality of life for people with blocked or constricted arteries. Knowing the advantages, hazards, and long-term effects of a cardiac stent treatment is crucial before having it. You may make informed decisions, actively participate in your treatment plan, and take the required actions to maintain a healthy heart by being aware of these fascinating facts. Always seek personalized guidance from your healthcare professional based on your unique situation.